Cell, Organ and Tissue Culture
Afshin Fathi; Manouchehr Barak; Mahshid Damandan; Firouz Amani; Rouhallah Moradpour; Irada Khalilova; Mehdi Valizadeh
Abstract
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) is one of the most common genetic deficiencies that affect approximately 400 million people worldwide. This study aimed to identify neonates with G6PD deficiency in Ardabil province during 2017-2018. This cross-sectional study was conducted on all term and preterm ...
Read More
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) is one of the most common genetic deficiencies that affect approximately 400 million people worldwide. This study aimed to identify neonates with G6PD deficiency in Ardabil province during 2017-2018. This cross-sectional study was conducted on all term and preterm newborns in Ardabil Province from April 2018 to April 2019. The sampling method was census and in study duration, 1044 newborns were entered in the study. For each infant, severe hyperbilirubinemia (total serum bilirubin equal or greater than 300 micromol/L) was tested by the diazo method and G6PD was evaluated by Fluorescent Spot Test (FST). Of all infants, 15 (1.4 %) were diagnosed to have G6PD deficiency by FST. The prevalence of G6PD deficiency was significantly in boys higher than in girls (80% vs. 20%, p=0.001). Of all infants, 97 (9.3%) had jaun dice 72 hours after birth that of them 7 neonates (7.2%) had G6PD deficiency. Results showed that the prevalence of G6PD deficiency in this study was less than in other places in Iran that may be because of different ethnicity and demographic features.

Phytochemistry and Biosynthesis
Ali Salehi-Sardoei; Halimeh Khalili
Abstract
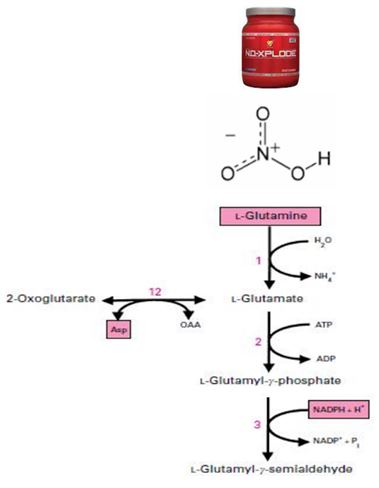
Nitrogen monoxide or nitric oxide is a biological active growth regulator that a wide range of studies have recently shown that it acts as a growth regulator (signaling molecule) in plants. As soon as Nitric Oxide (NO) known as a new biological agent in plants and animals, biological branches of sciences ...
Read More
Nitrogen monoxide or nitric oxide is a biological active growth regulator that a wide range of studies have recently shown that it acts as a growth regulator (signaling molecule) in plants. As soon as Nitric Oxide (NO) known as a new biological agent in plants and animals, biological branches of sciences like medicine, biochemistry, physiology and genetics have paid special attention to it. NO is a very reactive gas shape free radical which has attracted much attention during recent years. This compound is produced by the plant and it has increased the shelf life of some fruits, vegetables and cut flowers in low concentrations. NO is mostly synthesized from enzymatic and non-enzymatic pathways whose enzymatic biosynthesis pathway is done by reductase nitrate biosynthesis pathway through the cytosol, also it is known as an important and very reactive signaling molecule with short life which is produced by a group of enzymes known as synthesize NO which transforms L-arginine to L-citrulline and NO. It has been revealed that plants use NO as a growth regulator which regulates and modifies antimicrobial defensive responses. Recently, it has been approved that this material plays a vital role in regulating the normal physiological activities of plants such as pores closing, aging, increasing the vase life of cut flowers after harvesting, respiration and photosynthesis, antioxidant enzymes activities and growth.
Medical
Kodipelly Ramana Raju; Afreen Sharifa; Paspula Soumya; Rumana Khanam; Koyala konda Banda Sanjay Bhargav
Abstract
The objective of the study is to compare and evaluate the efficacy of atorvastatin (group – A) versus rosuvastatin (group – B) on baseline parameters like lipid profile tests and to assess the risk of metabolic syndrome using a Mets calculator. A total of 100 patients were enclosed in the ...
Read More
The objective of the study is to compare and evaluate the efficacy of atorvastatin (group – A) versus rosuvastatin (group – B) on baseline parameters like lipid profile tests and to assess the risk of metabolic syndrome using a Mets calculator. A total of 100 patients were enclosed in the present study who met the inclusion criteria. They were divided into two groups based on their treatment plan Group A includes 24 males and 26 females while Group B includes 23 males and 27 females. The mean differences before treatment for group A and group B are as follows, HDL (31.52±0.35 and 28.34±0.480), LDL (161.4±1.09 and 163.16±0.94), Total cholesterol (252.82±1.09 and 255.56±1.26) and Triglycerides (214.2±0.86 and 215.98±0.62), VLDL (35.98±0.56 and 36.12±0.43). The mean differences after treatment for group A and group B are as follows HDL (39.92±0.46 and 42.04±0.30), LDL (144.96±0.68 and 138.34±0.73), Total cholesterol (181.48±1.98 vs 174.32±2.08), Triglycerides (185.94±1.22 vs 181.74±1.77), VLDL (27.14±0.21 and 24.72±0.27). Group B (P=0.001) exhibited a significantly greater reduction in cholesterol levels as compared to Group A (P = 0.002). The reductions in LDL, VLDL, Total Cholesterol, and Triglycerides along with increased HDL levels were found to be significantly more in the Rosuvastatin group. In this study, we observed that patients on Rosuvastatin exhibited better control over lipid profile when compared to patients who are on Atorvastatin. Since, this study was conducted on a smaller number of patients, to make consecutive remarks about the superiority of either of the treatment regimen; further analysis of clinical trials is required for appropriate selection of the best statin therapy.

Medical
Mohammad Mehdi Soltan Dallal; Zahra Rajabi; Mohammad Reza Mohammadi; Arezoo Bagheri Sadegi
Abstract
Foodborne diseases are a global problem that is spreading day by day. These diseases are one of the most common causes of death in children and the elderly. This study was conducted to investigate the prevalence of water and foodborne diseases in Kurdistan province for six months from April to September ...
Read More
Foodborne diseases are a global problem that is spreading day by day. These diseases are one of the most common causes of death in children and the elderly. This study was conducted to investigate the prevalence of water and foodborne diseases in Kurdistan province for six months from April to September 2022. Stool samples from patients were collected in the laboratory in a special container containing 10% formalin preservative. 134 stool samples from 28 food outbreaks from Kurdistan province were analyzed for the type of infected bacteria. The research results were analyzed in SPSS-19 software. Among the 28 outbreaks in Kurdistan province during the two seasons of spring and summer, the highest number of outbreaks was in the summer season with 20 and then in the spring season with 8 outbreaks. The dominant age group was children under 10 years (%21) old and people between 20-30 years old, and the dominant gender group was men. The most common clinical symptoms were nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, bloody diarrhea and non-bloody diarrhea. It is important to know the type of bacteria that cause water and foodborne diseases in reducing outbreaks and treatment costs and applying necessary measures for control and prevention.

DNA, RNA, protein components
Masoud Tourang; Le Fang; Yuan Zhong; Ram Chandra Suthar
Abstract
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers known, and it is also a significant cause of death in women. If breast cancer is diagnosed in the early stages of the disease and treated appropriately, we can see an increase in life expectancy for more than 90% of patients. Research on molecular biomarkers ...
Read More
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers known, and it is also a significant cause of death in women. If breast cancer is diagnosed in the early stages of the disease and treated appropriately, we can see an increase in life expectancy for more than 90% of patients. Research on molecular biomarkers with enough sensitivity and specificity can be a good solution for rapid diagnosis in the clinical stage. Meanwhile, endogenous retroviral biomarkers can have good functional benefits. Human Endogenous Retroviruses as heterochromatin fragments of the genome usually lack expression, but in several types of human cancers, including breast cancer, HERV-Kenv mRNA is significantly increased. This study used RT-PCR to detect the expression of HERV-K mRNA and tried to introduce screening tools for the early detection of breast cancer. In this case-control study, blood samples of 50 patients with hospitalized breast cancer and 50 healthy individuals were designed to evaluate the expression of HERV-Kenv mRNA using specific primers and were analyzed by RT-PCR. PCR test was optimized as a positive control using Hela cancer cell line (cervical adenocarcinoma), which expresses the HERV-Kenv gene. Studies on both patient and control groups showed that the increase in mRNA expression was positive in 64% of patients with breast cancer and negative in all healthy individuals. The results indicate an increase in the expression of endogenous human retroviruses (HERVs) in breast cancer. Because the amount of HERV-Kenv mRNA in the blood of breast cancer patients increases dramatically, it is predicted that these mobile genetic elements could be used as a diagnostic biomarker.

Medical
Musa Yakubu Tula; Joel Filgona; Serah Erold Kyauta; Richard Elisha
Abstract
The ability of the bacterial isolate to cause debilitating effects on the host is intricate and is a function of many factors, particularly that of the host and the bacteria. Among the bacterial factors are the virulence mechanisms. As such this research was a cross-sectional study conducted between ...
Read More
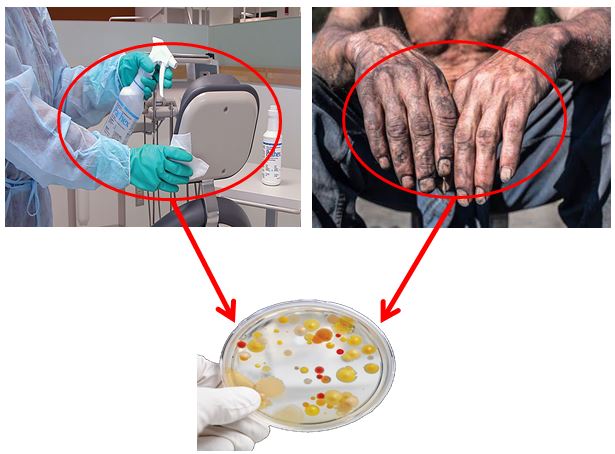
The ability of the bacterial isolate to cause debilitating effects on the host is intricate and is a function of many factors, particularly that of the host and the bacteria. Among the bacterial factors are the virulence mechanisms. As such this research was a cross-sectional study conducted between October–December 2021 to establish the existence of virulence determinants on bacterial isolates from hospital fomites and the hands of healthcare workers. To achieve this, 100 samples (including sink, beddings, door handles, benches, and hands of healthcare workers) from children, female and male wards of Mubi General Hospital were analyzed for bacterial growth and were identified by standard procedure. Isolates were subsequently screened for virulent determinants (hemolysis, hemagglutination, biofilm production, and heteroresistance) phenotypically by standard methods. From the 72 bacterial isolates recovered, 23(31.9%) were biofilm-producing organisms. Of these, 15(20.8%) and 8(11.1%) were moderate and high biofilm-producing organisms respectively with no statistical difference (P=0.665). Pseudomonas aeruginosa (13.9%) was the most predominant biofilm-producing organism. Furthermore, hemolysin production was predominant in Staphylococcus aureus (71.4%), while positive hemagglutination reaction was predominant in P. aeruginosa (38.5%). Sixteen (16) bacterial isolates showed heteroresistance (HR) to various antibiotics; of these, Escherichia coli (43.8%) constitute the majority of the isolates. The expression of such virulence determinants by bacterial isolates in the study area may constitute a health risk to patients and hamper the quality of health care delivery.

System Biology
Ismail Muhammad; Muinat Abdullahi Muhammad; Rejoice Asher; Abdulmalik Bala Shuaibu
Abstract
This research aimed to evaluate the larvicidal activity of the lower doses of commercially synthetic Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis (Vectobac 12 Aqueous Solution (12AS)) against the fourth instar larva. One hundred and fifty blood-fed female anopheles mosquitoes were collected from different resting ...
Read More
This research aimed to evaluate the larvicidal activity of the lower doses of commercially synthetic Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis (Vectobac 12 Aqueous Solution (12AS)) against the fourth instar larva. One hundred and fifty blood-fed female anopheles mosquitoes were collected from different resting sites from Abuja Quarters in June 2022 using an aspirator and allowed to breed until the first instar larva appeared. The larvae were monitored and fed with 10% yeast until the third instar emerged. 240 healthy third instar larvae were selected and grouped into three treatments containing sixty (60) larvae each and replicated three times. The first, second and third treatments were respectively treated with 0.84, 0.42 and 0.21ml/l of Vectobac 12AS. Each treatment has a control containing twenty (20) larvae. Larval mortality was determined using a glass rod at an interval of 15 minutes for 24 hours. ANOVA was used to statistically analysed differences in the larval mortality between the treatment and probit analysis was used to determine the lethal concentration (LC) and the lethal time (LT). Mortality of 1(6.7%) and 3(5.0%) were observed in the first treatment (0.84ml/l) after 15 and 30minute of exposure respectively. The highest mortality of 60(100%) was observed in all the treatments after 24 hours of exposure. Statistically, there was no significant difference (F=0.081, P> 0.05). 2.35 ml/l, 5.54 ml/l and 8.15 ml/l was determined to be LC50, LC90 and LC99 respectively and LT50, LT90 and LT99 were found to be, 1809.29min and 2451.34min respectively. Conclusively vectobac 12AS has demonstrated a high level of efficacy as it revealed 100% larval mortality even at a lower recommended dose. Further research should be carried out to study the impact of other biological and environmental factors on the efficacy of vectobac 12AS.

Nano-Biotechnology
Mehran Alavi; Mahendra Rai; Fleming Martinez; Danial Kahrizi; Haroon Khan; Irwin Rose Alencar de Menezes; Henrique Douglas Melo Coutinho; José Galberto Martins Costa
Abstract
The applications of nanoparticles in various practical fields, owing to their unique properties compared with bulk materials, have been occupying the minds of scientists for several decades. In this regard, a combination of pharmacology and nanotechnology has contributed to producing newer effective ...
Read More
The applications of nanoparticles in various practical fields, owing to their unique properties compared with bulk materials, have been occupying the minds of scientists for several decades. In this regard, a combination of pharmacology and nanotechnology has contributed to producing newer effective anticancer and antimicrobial agents to inactivate resistant cancer cells and microorganisms, specifically multidrug-resistant ones. The physicochemical properties of nanoparticles based on metalloid, metal, and metal oxides such as selenium, silver, gold, titanium dioxide, zinc oxide, copper oxide, platinum, and magnesium oxide, have been well known and referred to as anticancer and antimicrobial agents or carriers. The inactivation and eradication of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria may be mainly resulted from the oxidative damages in the bacterial medium. Overall, metalloid, metal and metal oxide NPs can be functionalized by other antibacterial or anticancer agents and biocompatible stabilizers to increase their efficiency in physiological conditions. However, the undesirable cytotoxicity of these nanoparticles in physiological conditions is the major hindrance to their application in the pharmaceutical industry and therapeutics. Nevertheless, it is expected that these problems will be solved in the near future. Therefore, the main objective of this review is to report an overview of the recent signs of progress in increasing anticancer and antibacterial mechanisms of metal and metal-based nanoparticles.

Cell, Organ and Tissue Culture
Ismael Bilal; Sijia Xie; Muna S Elburki; Zahra Aziziaram; Sangar Muhammad Ahmed; Salah Tofik Jalal Balaky
Abstract
Glioblastoma is a fatal brain tumor, and the standard treatment for this cancer is the surgical removal of the tumor followed by chemotherapy with temozolomide and radiotherapy. Because chemotherapy has many side effects, the use of compounds extracted from natural herbs, due to fewer side effects, can ...
Read More
Glioblastoma is a fatal brain tumor, and the standard treatment for this cancer is the surgical removal of the tumor followed by chemotherapy with temozolomide and radiotherapy. Because chemotherapy has many side effects, the use of compounds extracted from natural herbs, due to fewer side effects, can be a good alternative or supplement to chemical drugs in cancer treatment. In this study, curcumin (diferuloylmethane), known as the main active ingredient of turmeric, was used to evaluate its cytotoxicity on four human glioblastoma cell lines (U373, U251, D54, and T98G). Among these cell lines, U373 was temozolomide resistance, and T98G was photodynamic treatment resistance. These cell lines were treated with increasing concentrations of diferuloylmethane. Survival percentage was assessed by MTT assay and the trypan blue staining method was used to evaluate the rate of cell death and confirm the results of the MTT assay. The results showed that diferuloylmethane has a cytotoxic effect on U251, D54, and T98G cell lines. This effect was higher in high concentrations of diferuloylmethane on U251 and D54 than on U373. Therefore, according to the results of the current study and further studies, curcumin (diferuloylmethane) can be considered an effective complementary treatment in the treatment of glioblastoma.

Medical
Hateme Alavi; Farzaneh Zaheri; Roonak Shahoei
Abstract
Childbirth is one of the most important experiences in the life of mothers, which can bring tensions and worries due to physical and psychological changes. Therefore, the present study was conducted to determine the amount of support and control during childbirth and attachment after birth in mothers ...
Read More
Childbirth is one of the most important experiences in the life of mothers, which can bring tensions and worries due to physical and psychological changes. Therefore, the present study was conducted to determine the amount of support and control during childbirth and attachment after birth in mothers who were referred to comprehensive health centers in Bijar County, in 2019. In this descriptive-analytical study, the studied population consisted of all the mothers who were referred to the comprehensive health centers of Bijar, who had passed 28 days after giving birth. The participants in the study were available to choose and completed the questionnaires for support and control during childbirth and attachment after birth. The collected data were analyzed using SPSS statistical software version 22 and multiple regression statistical tests, and a significance level of p<0.05 was considered. The results of the study showed that the level of support and control during childbirth was 83.32±17.038 and the level of attachment after birth was 47.70±4.688. Also, the results of the study showed that none of the investigated demographic variables were related to support and control during childbirth. The type of delivery (vaginal delivery with episiotomy r=-2.226, p=0.012) and the baby's gender (r=9.927, p=0.047) were related to support and control during delivery. Also, the results showed that among the demographic variables examined with attachment after birth, the variable of income (equal to monthly expenses r=6.307, p=0.01) had a positive and significant relationship with attachment after birth. The findings showed that support and control are at a moderate level and attachment after birth is at an average level, so it seems that with the necessary training on the importance of mother and child attachment to medical personnel, an effective step can be taken to improve these two factors and their consequences.

Bioinformatics
Wenyuan Li; Yao Wang
Abstract
Stress granules (SGs) will be produced when the body is under external stimuli, and SGs play an important role in the pathogenesis of more and more diseases. The study on SGs has generally grown to a comprehensive subject in the past 35 years (from 1988 to 2022). The bibliometric analysis was used to ...
Read More
Stress granules (SGs) will be produced when the body is under external stimuli, and SGs play an important role in the pathogenesis of more and more diseases. The study on SGs has generally grown to a comprehensive subject in the past 35 years (from 1988 to 2022). The bibliometric analysis was used to comprehensively analyze the progress and development trend of SGs research. The literature output in the field of peritoneal dialysis showed a fluctuating growth in the past 35 years, and the last five years were the peak period of literature output. Journal of virology was the most widely published journal on SGs. And the most common research category was Biochemistry Molecular Biology. No matter in terms of the number of papers, citation frequency, H-index, or the distribution of journals and funding sources, the United States was far away from leading. With the enhancement of economic and scientific research strength, China has gradually carried out research on SGs. However, the citation frequency and H-index of Chinese papers were relatively low. Research cooperation between research institutions was relatively close, but domestic research institutions had less cooperation with relevant international institutions. The cooperation among authors was relatively scattered, and further exchanges and cooperation between scholars were needed for Chinese scholars. There are more and more reports about SGs, but there was still a big gap between China and the United States in the study of SGs.

Genetic engineering
Hamid Ahani; Soroush Attaran
Abstract
Seabuckthorn has multiple-use properties. This review explores the medicinal applications of Hippophae rhamnoides in healing ailments. The plant is being used in different parts of the world for its nutritional and medicinal properties. Sea buckthorn-based preparations have been extensively exploited ...
Read More
Seabuckthorn has multiple-use properties. This review explores the medicinal applications of Hippophae rhamnoides in healing ailments. The plant is being used in different parts of the world for its nutritional and medicinal properties. Sea buckthorn-based preparations have been extensively exploited in folklore treatment of slow digestion, stomach malfunctioning, cardiovascular problems, liver injury, tendon and ligament injuries, skin diseases and ulcers. In recent years, the medicinal and pharmacological activities of Seabuckthorn have been well investigated using limited clinical trials. Homeopathy is a well-respected modality to assist wellness. Traditional and modern medicinal experts have been applied this plant to treat various diseases. Seabuckthorn is an important plant because of its immense medicinal and therapeutic potential. However, several knowledge gaps identified in this paper would give impetus to new academic and R&D activities, especially for the development of Sea buckthorn-based herbal medicine and nutraceuticals. Its full application in dermatology may be attributed to the presence of a variety of flavonoids, vitamins, and unsaturated fatty acids. Great use of the plant in the traditional system for dermatological aspects, demands further comprehensive phytochemical work based on its actual use by the traditional population. Anti-inflammation is the most important applicable ingredient of this miracle berry.

Gene Expression Studies
Zahra Aziziaram; Ismael Bilal; Yuan Zhong; Azzadin Kamal Mahmod; Mohammad Reza Roshandel
Abstract
Naproxen is a common analgesic and antipyretic medication that is widely used around the world. This medicine at high doses leads to liver and kidney necrosis in humans and animals. The mechanism of kidney damage, unlike liver damage, is not well understood and is one of the most common causes of emergency ...
Read More
Naproxen is a common analgesic and antipyretic medication that is widely used around the world. This medicine at high doses leads to liver and kidney necrosis in humans and animals. The mechanism of kidney damage, unlike liver damage, is not well understood and is one of the most common causes of emergency department patients. Therefore, in the present study, the protective effect of curcumin, a compound derived from turmeric, was investigated on renal damage caused by naproxen. For this purpose, 25 male Wistar rats were selected and were randomly divided into five groups. Naproxen was dissolved in a 5% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) solution and was injected intraperitoneally at 1000 mg/kg of animal weight. Also, curcumin was dissolved in 5% DMSO and was injected within peritoneum at a dose of 200 mg/kg of animal weight into the relevant groups. After 24 hours of injection, rats were bled and plasma urea and creatinine levels were measured. The rate of lipid peroxidation, the activity of superoxide dismutase and catalase in the kidney, total plasma antioxidant capacity, and PGC-1α gene expression were measured. The results showed that naproxen significantly increased the levels of biochemical markers of urea and creatinine in plasma and lipid peroxidation in the kidney; also, it decreased the activity of the antioxidants enzymes. The use of curcumin in naproxen-exposed groups significantly reduced the concentrations of urea, creatinine, and lipid peroxidation. Curcumin increased the activity of catalase, superoxide enzymes, and the total antioxidant capacity of plasma. Also, curcumin increased the expression of the PGC-1α gene, which reduces the effects of naproxen. Therefore, according to the current study results, curcumin could significantly reduce the harmful effects of naproxen on the kidneys. However, in future studies, the effect of curcumin should be evaluated on the naproxen mechanism in the treatment of those patients who need naproxen.

Biochemistry
Huda Kadhim Jaafer; Melike Bilgi Kamac; Abdulnasser Mohammed Al-Gebori
Abstract
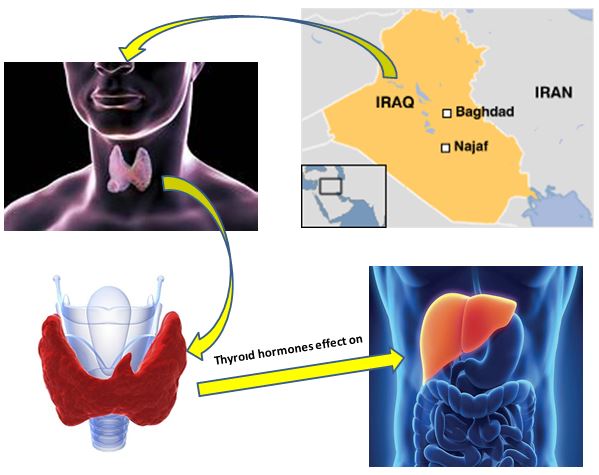
This study was aimed to study the effect of thyroid hormones on some biochemical tests of liver function in Iraqi male patients and to study the relationship between them. A controlled study included 135 samples from patients and controls, group B, 45 patients with a liver disorder, and group C: 45 patients ...
Read More
This study was aimed to study the effect of thyroid hormones on some biochemical tests of liver function in Iraqi male patients and to study the relationship between them. A controlled study included 135 samples from patients and controls, group B, 45 patients with a liver disorder, and group C: 45 patients with a thyroid disorder, and group A: 45 healthy people (as the controls group). The study concluded that there were significant statistically significant differences for patients with liver disease, as well as for patients who suffer from abnormalities in the functions of the thyroid gland. For triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), there was clear importance and a slight impact for patients with liver disease. Because of the defect in the liver enzymes, this led to an increase in the TSB percentage, which increased significantly. Alkaline and Albumin levels indicate statistical significance within the results of our study. Serum protein levels had no significant changes in our study.
Medical
Mehdi Kakaei; Fazal Ur Rehman; Farzaneh Fazeli
Abstract
Legumes provide a major portion of protein and calories in the diet of many people around the world. Among different legumes, chickpeas have higher bioavailability and protein. Legumes are the second most important source of human food after the cereal family. Among them, chickpea with 15 to 25% of protein ...
Read More
Legumes provide a major portion of protein and calories in the diet of many people around the world. Among different legumes, chickpeas have higher bioavailability and protein. Legumes are the second most important source of human food after the cereal family. Among them, chickpea with 15 to 25% of protein rich in essential amino acids such as arginine, leucine, isoleucine, lysine, valine, threonine, meotine and cysteine, phenylalanine and tyrosine, this plant causes fertility due to nitrogen fixation. The content chickpea is not only a source of protein, but also a source of dietary fiber, resistant starch, polyunsaturated fatty acids, vitamins and minerals, especially folate, calcium, magnesium and potassium. Regarding chickpea milk, plant milk consumers have accepted chickpea extract well. Due to the effective compounds, it is necessary to study the process of human health. In this research, the evaluation of published articles was used and the extracts of these studies were used to compile this article. Reading this article inspires the reader with a favorable view about planting peas in the field and their properties in the body. It is recommended that according to the properties of chickpeas, food industry researchers, plant breeding researchers and other related experts should provide more extensive research works to identify its useful aspects for the healthy and organic production of this valuable plant. Finally, it should be seriously included in the household basket to have a healthy human body.

Gene Expression Studies
Muhammed Furkan Ercisli; Gao Lechun; Sarhang Hasan Azeez; Rebwar Muhammad Hamasalih; Siyan Song; Zahra Aziziaram
Abstract
Rivaroxaban is an anticoagulant drug that prevents forming of blood clots. In addition, it can be administered to prevent and treat thrombotic diseases such as atrial fibrillation, cardiac arrhythmia, heart valve disease, orthopedic surgery, and thrombophilia to reduce the risk of thrombosis. Various ...
Read More
Rivaroxaban is an anticoagulant drug that prevents forming of blood clots. In addition, it can be administered to prevent and treat thrombotic diseases such as atrial fibrillation, cardiac arrhythmia, heart valve disease, orthopedic surgery, and thrombophilia to reduce the risk of thrombosis. Various factors such as age, gender, diet, medications, and genetic factors effectively determine the dose of rivaroxaban. Genetic variability in drug-metabolizing enzymes, including the cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes and especially CYP3A4, has been associated with rivaroxaban response. The current study aimed to identify the frequency of CYP3A4 common polymorphisms, as well as their association with rivaroxaban response in 100 patients of Arab descent (48.6% female). CYP3A4 gene polymorphisms were examined by the PCR-RFLP method, and the findings were analyzed by SPSS 16 software and t-test. The frequency of CYP3A4*1B/*1B, CYP3A4*1B/*1A, CYP3A4*1B/*1C, and CYP3A4*1A/*1C was 67.35%, 10.64%, 19.12% and 2.89%, respectively. According to our results, CYP3A4 *1B/*1B genotype was the most common, and patients with CYP3A4*1B/*1B alleles needed a higher daily dose of rivaroxaban than *1B/*1A, *1B/*1C, and *1A/*1C carriers (9.57 ± 1.54 mg/day, P=0.015). Therefore, according to the results, CYP3A4 gene polymorphism has an important effect on the dose of rivaroxaban required to maintain the International Normalized Ratio (INR) in the range of 2-3.

Cell structural and functions
Hamid kheyrodin; Raheba Jami; Fazal Ur Rehman
Abstract
Plant cells are the basic unit of life in organisms of the kingdom Plantae. These organisms as eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus along with particular structures called organelles that perform various functions. The plant cell wall can provide a structural framework to support plant ...
Read More
Plant cells are the basic unit of life in organisms of the kingdom Plantae. These organisms as eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus along with particular structures called organelles that perform various functions. The plant cell wall can provide a structural framework to support plant growth and defense the cells against various viral and bacterial pathogens. The cell wall can retain flexibility, also when subjected to developmental, biotic, abiotic stimuli, and stresses it can be efficiently remodeled in response. Genes encoding enzymes are able to fabricate or hydrolyze substances of the plant cell wall exhibit differential expression when subjected to different stresses, suggesting they may facilitate stress tolerance such as heavy metals, dust accumulation, and salty medium through changes in cell composition wall. Bacteria are small single-celled organisms that get the nutrients they need from their environment. Sometimes, this environment can be your child or any other living thing. Bacteria are very small and cannot be seen under a microscope. Bacteria help the digestive system and prevent harmful bacteria from entering the human body as well as some other bacteria are also applied to produce drugs and vaccines. A cell wall as the non-living component can cover the outmost layer of a cell. According to the type of organism, the cell envelope has a different composition. The cell envelope separates the interior contents of the cell from the exterior environment. In addition, it provides shape, support, and protection to the cell and its organelles. However, this cellular component is present exclusively in eukaryotic plants, fungi, and a few prokaryotic organisms. Compounds found in plant cells are absent in animal cells, and DNA base sequences reflect this. Moreover, plant DNA is often larger than animal DNA. In this mini-review, we concluded that the differences between plant and animal DNA defendant on the sequence of bases in the helix.
Nano-Biotechnology
Mehran Alavi; Michael R. Hamblin
Abstract
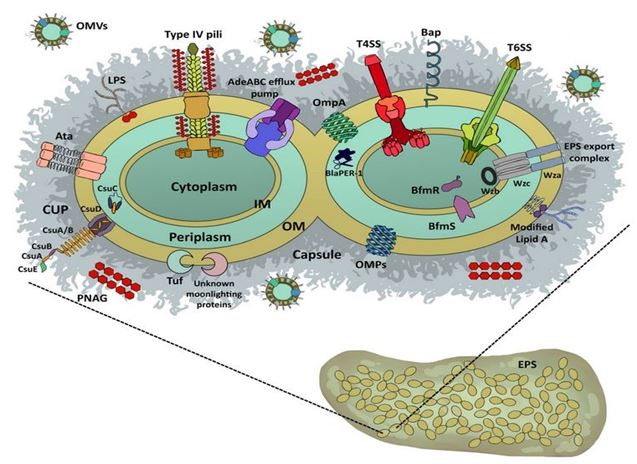
Various microorganisms are located on the human skin, mucous membrane and inside the human body. Many of these microorganisms are beneficial and few are even essential, however, some pathogens are known to cause infection and have the ability to attack and damage the host tissue. Treatment of infectious ...
Read More
Various microorganisms are located on the human skin, mucous membrane and inside the human body. Many of these microorganisms are beneficial and few are even essential, however, some pathogens are known to cause infection and have the ability to attack and damage the host tissue. Treatment of infectious bacterial disease by antibiotics is one of the major conventional strategies. Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria have developed resistance to conventional antibiotics by various mechanisms, including overexpression of efflux pumps, preventing drug penetration into the cells, genetic mutations, increased production of competitive inhibitors of antibiotics, or overexpression of enzymes that inactivate or hydrolyze antibiotics. Consequently, finding a new approach to overcome these hindrances is vital for the treatment of severe bacterial infections. Nanomaterials can be effective therapeutic compounds, with unique properties compared to bulk materials. Metal and metal oxide nanoparticles, particularly silver nanoparticles, have demonstrated strong antibacterial activity against most (if not all) multidrug-resistant bacteria. Several antibacterial mechanisms have been proposed for these nanoparticles, however, their interaction with bacterial nucleic acids is not completely understood, so this review discusses recent advances in this area.

Medical
Namrata Malik; Umesh Pravin Dhuldhaj
Abstract
The sudden outbreak of coronavirus turned into a pandemic and resulted in huge socio-economic and human losses becoming a public health emergency. It took just 3-4 months to spread and encroach all over the world and not even a single country is left was unaffected by the coronavirus. WHO started clinical, ...
Read More
The sudden outbreak of coronavirus turned into a pandemic and resulted in huge socio-economic and human losses becoming a public health emergency. It took just 3-4 months to spread and encroach all over the world and not even a single country is left was unaffected by the coronavirus. WHO started clinical, epidemiological, and laboratory investigations in response to this outbreak to control the further spread of the virus. The coronaviruses are enveloped and pleomorphic. The spike proteins present on the virus surface mediate its entry into host cells. The vaccines recommended have been shown to reduce COVID-19 illness symptoms but somehow their role in the transmission of the disease is unclear. By contrast, immunomodulatory therapy has also benefitted patients. As long as SARS-CoV-2 spreads in the population there are chances of its mutation as RNA viruses mutate over time and its upcoming variants. The previous Delta variant and the latest Omicron variant may cause much more serious deaths and health issues. Variants reduce the effectiveness of monoclonal antibodies or antibodies generated by previously administered vaccines. This review focuses on the pathogenicity of coronavirus and various drug therapies available to date to cure the disease. The present study also highlights the target sites and side effects of available drugs for treating COVID-19.

Cell, Organ and Tissue Culture
Sarhang Hasan Azeez; Sarwar Nawzad Jafar; Zahra Aziziaram; Le Fang; Ahang Hasan Mawlood; Muhammed Furkan Ercisli
Abstract
Recently, stem cells have been considered renewable cell sources in the treatment of diabetes and the development of insulin-producing cells. In this regard, the current study aimed to compare Insulin-producing cells from bone marrow stem cells with injectable insulin in rats with type I diabetes. For ...
Read More
Recently, stem cells have been considered renewable cell sources in the treatment of diabetes and the development of insulin-producing cells. In this regard, the current study aimed to compare Insulin-producing cells from bone marrow stem cells with injectable insulin in rats with type I diabetes. For this purpose, 40 rats were divided into four groups: the control or healthy group, the diabetic control group, the group that received differentiated insulin-producing cells from bone marrow, and the group that received insulin treatment. To differentiate insulin-producing cells from bone marrow, the femoral bone marrow of rats was extracted using the flushing method. Differentiated cells were evaluated using dithizone-specific dye, anti-insulin-proinsulin antibodies, and anti-insulin beta receptors. Also, the expression of the pdx-I gene, as the specific gene of pancreatic cells, was examined by RT-PCR. The results showed that transplantation of insulin-producing cells could significantly increase blood insulin levels in diabetic rats. This increase intensified in the second stage of transplantation when more cells were injected into rats. Concerning decreasing blood sugar levels, differentiated cells were able to reduce blood sugar levels significantly. Even in the first stage of cell injection, in which the rats received a small number of cells, their blood sugar levels were controlled by these cells. As a result, the present study showed that repeated transplants of insulin-producing cells differentiated from bone marrow could decrease blood sugar and increase insulin levels.

Gene Expression Studies
Ismail Muhammad; Pukuma Micah Sale; Muhammad Khadija Salisu; Tanko Mahmoud Muhammad; Bala Abubakar; Augustine Linda Maidala; Enock Nuwanyada
Abstract
Chloroquine was one of the most cheapest and effective chemotherapeutic drugs for Plasmodium falciparum-malaria, but for a long, the drug has been officially withdrawn in almost all malaria-endemic countries including Nigeria, due to the development of resistance by the parasite. Withdrawal of the drug ...
Read More
Chloroquine was one of the most cheapest and effective chemotherapeutic drugs for Plasmodium falciparum-malaria, but for a long, the drug has been officially withdrawn in almost all malaria-endemic countries including Nigeria, due to the development of resistance by the parasite. Withdrawal of the drug may make the drug regains its efficacy. Therefore, this study aimed to determine the presence of Biomarkers associated with chloroquine resistance from Gombe Local Government Area, Gombe State, Nigeria after its withdrawal in 2005. Twenty hundred blood samples were collected from consented study subjects and analysed using Microscopy, RDT and PCR. DNA was extracted using Quick-DNA™ Miniprep (No. D4069), Purity and Concentration of the DNA were determined using Nanodrop Spectrophotometer. 57 true positive samples were selected for molecular analysis. Nested PCR was used to amplify the required codon (C72S, M74I, K76T and N75E) position of PCRT the gene of P. falciparum. Both Primary and Secondary PCR was carried out. The PCR products were subjected to electrophoresis in 2% agarose and stained with ethidium bromide. The amplicons were purified and sequenced, after which the sequenced products were subjected to BLAST software. Single Nucleotide Polymorphism was recorded from C72S and K76T with a prevalence of 05(8.80%) and 46(80.70%) respectively. Confirmed biomarkers of Chloroquine resistance are still present in P. falciparum isolate from Gombe L.G.A.

Bioinformatics
Sahand Sasani; Sajad Rashidi Monfared; Ali Reza Mirzaei
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small (~22 nucleotides) non-coding endogenous RNA molecules that negatively regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level by degrading the target protein-coding mRNA genes or suppressing translation in plants, which consequently participate in a variety of biological ...
Read More
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small (~22 nucleotides) non-coding endogenous RNA molecules that negatively regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level by degrading the target protein-coding mRNA genes or suppressing translation in plants, which consequently participate in a variety of biological and metabolic processes in both animals and plants. Detection of miRNAs is chiefly carried out by microarray, real-time-PCR, northern blot, and bioinformatics approaches. Bioinformatics or in silico-based approaches are the easiest and cheapest ways to identify desired miRNAs. In this study, several miRNAs in Echinophora platyloba were identified, and their potential roles were reported. E. platyloba, which belongs to the Umbelliferae family, is an endemic plant in Iran found in the Kermanshah, Hamedan, and Lorestan provinces; it has important medicinal uses such as cytotoxic activity in breast cancer, treatment of dysmenorrhea, central and peripheral analgesic effects, and hepatoprotective effects on acute acetaminophen-induced liver injuries. To this end, the RNA was extracted from E. platyloba leaf and sent to the Beijing genome institute for RNA sequencing. After quality control, low-quality data was filtered, and de novo assembly was performed. Detection of miRNAs was then performed by miRDeep (v37) and miRBase tools. Accordingly, we identified seven miRNAs from the leaf dataset, and their secondary structures were evaluated. Target genes of the detected miRNAs were identified through the psRNA target website.

Nano-Biotechnology
Mehran Alavi; Mahendra Rai
Abstract
Finding efficient therapeutic strategies to fight antibiotic-resistant bacteria is a complicated affair specifically in the therapy of chronic bacterial infections related to hospital-acquired infections. Recently, three major antibacterial systems based on antisense RNA, CRISPR-Cas9, and metal/metal ...
Read More
Finding efficient therapeutic strategies to fight antibiotic-resistant bacteria is a complicated affair specifically in the therapy of chronic bacterial infections related to hospital-acquired infections. Recently, three major antibacterial systems based on antisense RNA, CRISPR-Cas9, and metal/metal oxide nanoparticles particularly silver (Ag) nanoparticles have shown more effective antibacterial activity compared to conventional antibiotics. ROS generation, attachment to the cell membrane, disruption of bacterial envelop, inactivation of electron transport chain, decreasing the local pH, modulation of cell signaling, and denaturation of biological macromolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids have been found as the main antibacterial functions of Ag nanoparticles. Antisense RNA, a single-stranded RNA, can hybridize with complementary genes in messenger RNA (mRNA) followed by blockage translation of these genes into proteins. Moreover, CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) is a family of viral DNA sequences derived from bacteriophages, which can target and destroy foreign DNA by nuclease activity. There are 2 classes and 6 subtypes (I-VI) of CRISPR-Cas systems, which may be engineered as potential antibacterial agents to target specific sequences. Therefore, here, recent advances and challenges for the antibacterial application of these three therapeutic agents are presented.

Biochemistry
Tamara Ahmed Abd Al-Kareem; Shaimaa Ahmad Hassan; Saifaldeen Muwafag Abdalhadi
Abstract
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a popular illness in women after puberty age. It’s described via overdone androgen production, and ovulation unrest while elevating metabolic syndrome. PCOS was usually diagnosed by Ultrasound or blood test to check the androgens and other hormone levels. There ...
Read More
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a popular illness in women after puberty age. It’s described via overdone androgen production, and ovulation unrest while elevating metabolic syndrome. PCOS was usually diagnosed by Ultrasound or blood test to check the androgens and other hormone levels. There are many causes of having pathogenesis of POCS which was related to abnormalities in hormone levels, insulin resistance, obesity, and others. the symptoms of PCOS could include irregular periods, excess body hair, weight gain, oily skin, and infertility. Due to the variety of symptoms, the POCS has many different types of treatment options, for instant use of medications or lifestyle changes such as weight loss. Many medications are used to treat PCOS like organic compounds and have proven effective in treating PCOS as well as many metallic elements will aid medicinal chemists in planning, organizing, and implementing new approaches toward the discovery of novel drugs. One of the most important medications which were used to treat PCOS is clomiphene citrate and that is commonly used for the treatment of infertility. This review highlights to the causes and treatments of PCOS and gives many examples of recent research that uses drugs and metallic elements as a medication.

Medical
Razieh Behzadmehr; Khadije Rezaie-Keikhaie
Abstract
Diabetes is one of the most common non-contagious diseases in the world. This disease is the fourth or fifth cause of death in most developed countries. The relationship between tuberculosis and diabetes had been introduced years ago and diabetes is considered a threatening factor in tuberculosis in ...
Read More
Diabetes is one of the most common non-contagious diseases in the world. This disease is the fourth or fifth cause of death in most developed countries. The relationship between tuberculosis and diabetes had been introduced years ago and diabetes is considered a threatening factor in tuberculosis in the research history. Not only tuberculosis is prevalent among diabetic persons, but also diabetes can affect the appearance of imaging of tuberculosis. This is a kind of analytic study, a case-control study, which was carried out between the years 2014 and 2015 in Zabol City. In this study, the radiographic findings from the patients suffering from pulmonary tuberculosis in diabetic patients and not diabetic patients are compared. These radiographic were handed to a radiologist and the radiologic findings of these graphs from the anatomic location (upper and lower half of the right and left bellows), Presence or absence of cavities, nodules, density and pleural involvement were recorded and compared with the diabetic and non-diabetic group. After gathering of the data using SPSS software, descriptive statistics were presented in the form of (frequency, percent) graphs and a chi-square test (p<0.05) was used to analyze and comparing of the results of diabetic and un-diabetic patients. The population of the study consisted of Chest radiographs for 124 TB patients which 61 (49.19 %) were suffering from diabetics. In this study, 45 (71.43%) non-diabetic and 42 (65.85%) diabetic patients were women (p=0.7). There were 12 diabetic TB patients (19.67%) and 3 non-diabetic- TB patients (4.76%) with the consolidation of middle part of left lung (p=0.01) and 8 (13.11%) diabetic TB and 1 (1.59%) non-diabetic TB with reticulonodular infiltration of lower part of left lung (p=0.02). There was no significant difference in the rest of the radiographic results. The findings of this study indicate that reticulonodular infiltration and consolidation of lower &middle parts of the lung in TB diabetic patients is more than in TB non-diabetic patients and diabetes can affect the findings of pulmonary tuberculosis radiography.


























